Do you know how to check the turbocharger by yourself once it stops work suddenly?
Here are some tips for your guidance.
1. Oil contamination
a) Mostly visible as scratches and score lines on the journal bearing and the shaft.
b) Inner and outer bore of the journal bearing becomes oversized and undersized respectively under this situation.
c) It results in excessive bearing tolerance between bearing and shaft, which contributes to a failed turbocharger.
Solution:
Always change the oil filters when replacing a new turbo. Use the correct oil grade for the engine and ensure that the inlet pipes are free from carbon deposits or sludge.
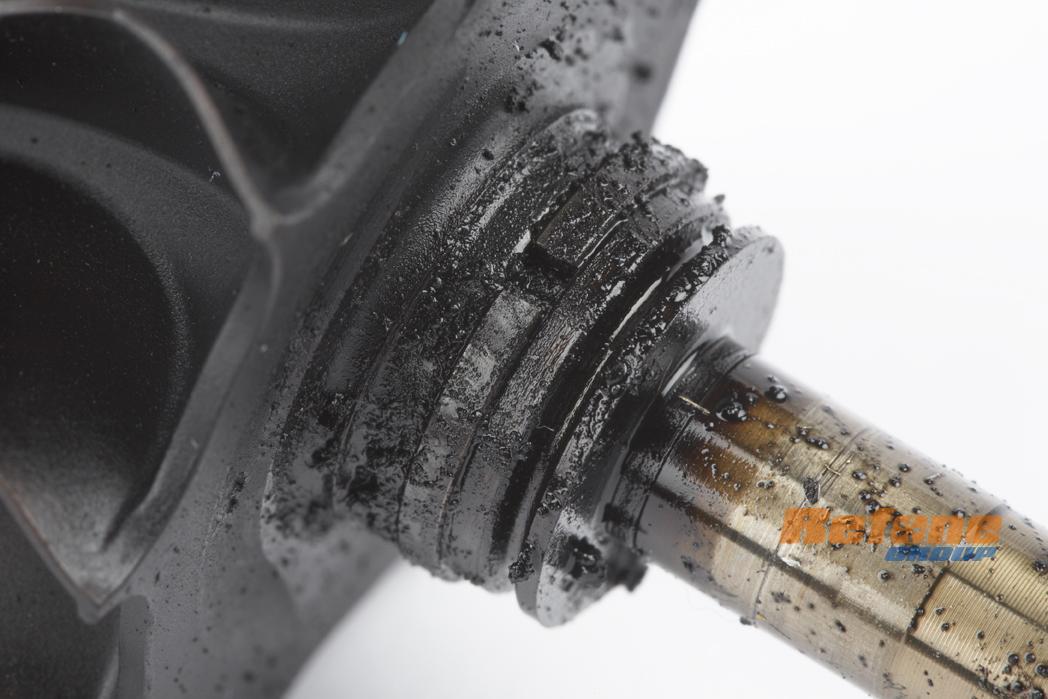


2. Presence of foreign objects
a) Damage to the compressor wheel
– Foreign objects may enter you turbocharger via the compressor inlet which can cause impact damage and abrasion to the compressor wheels.
b) Damage to the turbine wheel
– Generally caused by engine components
e.g Debris from corroded exhaust manifold, broken valves, melted pistons, valve seals, broken gaskets etc
Solution:
– Make sure that the induction system is free from any objects.
– No leftover particles from the previous turbo.
– Check the engine condition as per engine manufacturer’s service manual.
– Change the gaskets and air filter regularly.


3. Oil leakage
a) Sometimes caused by pressure build-up in the crankcase or oil sump.
b) This will restrict the oil flow from the turbocharger oil outlet where the pressure pushes the oil back into the bearing housing.
c) It results in engine oil penetrating through both end piston rings.
d) Restricted induction system also causes oil leakage from the compressor end.
e) Use of liquid gasket(silicone glue) on oil outlets will restrict the oil flow back to the oil sump/crankcase.
Solution:
While a failed turbochargerneeds immediate attention,
– Check the condition of the engine before replacing with a new turbocharger.
– Inadequate oil supply for the turbine bearings can happen at the compressor and turbine ends.
– If problem persists, it will eventually lead to turbo failure.
– To prevent this, ensure oil drain systems are free from obstructions and foreign particles.
– Use of liquid gasket is prohibited.
4. Oil delay
a) Frequently caused by failure to pre-crank the engine 3-4 times.
b) Immediate high engine speed upon initial start-up procedure.
c) Failure to install oil feed lines correctly.
d) Restricted or kinked oil feed lines.
e) Clogged oil cooler.
f) Clogged oil filter.
Solution:
– Pre-crank the engine 3-4 times.
– Do not accelerate the engine upon initial startup.
– Allow the engine to remain idle for at least 5 minutes.
– Replace any kinked oil feed lines.
– Clean the oil cooler, replace if found to be badly distorted or clogged.
– Change oil filter.
5. Oil starvation
a) Worn out oil pump or restricted oil cooler / oil feed lines may cause catastrophic damage to the turbocharger due to insufficient and inconsistent oil supply into the turbocharger.
b) In these situations, there is excessive friction between the shaft and bearing system.
c) Inner and outer bore of the journal bearing becomes oversized and undersized respectively. Hence causing the wheel to rub against the housing and failing to ensure a recommended tolerance.
Solution:
– Check oil pressure and oil supply to the turbo.
– Avoid using liquid gasket on oil inlet as it creates blockages in oil passages.
– Ensure consistent oil flow by replacing restricted, clogged oil inlet pipes.
– Change the oil pump if found to be faulty.
– Change new oil filter.
– Clean the oil cooler, replace if found badly distorted or clogged.
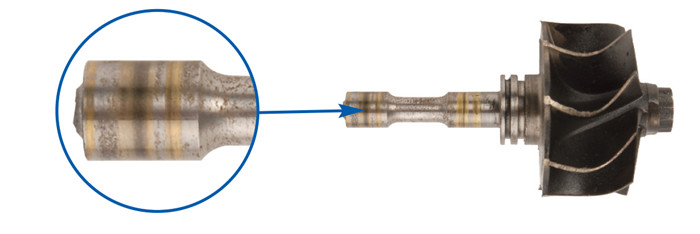
6. Overspeeding / Overboost
a) Obstruction within induction system, tampering with the wastegate, VNT linkage and actuator will force the turbocharger to operate past its safe operating parameters.
b) In some occasions, turbine wheels or compressor wheels may burst.
Solution:
– To prevent this, check that there are not restrictions or leakages in the air intake pipe work.
– Do not tamper with the wastegate or VNT linkage.
– Ensure that all electronic sensors and ECU are in working condition.
7. REA & SREA malfunction
a) If there is a suspected malfunction in REA or SREA, check for past service history and make sure ECU error codes and engine components are fixed and correctly replaced.
b) Check to see if the voltage of the battery or alternator is correct.
c) Check that the vane assembly-operating lever can move freely. If not, move the crank assembly multiple times to loosen it a little.
d) Reconnect the linkage and test again. Ensure that there is no water or stain underneath the connector seal and in REA/SREA connector.
e) Make sure that there are no cracks or damage on the REA/SREA connector walls. Turn on the ignition and check for the warning light signal, start the engine and look for REA movement. Look out for possible electrical faults if the warning light glows.
8. EGR Valve
a) A malfunctioning EGR valve can cause a disproportionate amount of carbon or soot at the turbine end, which will cause the VNT mechanism to fail.
b) Ensure EGR valve can open and close smoothly.
c) Air leakage in the vacuum or improper vacuum connection may cause the valve to not open.
d) If the valve refuses to close, it may be due to heavy deposits on the tappet, high pressure or inaccurate control resulting in overheating and damaging of the valve, or leakage and obstructions of the intake pipe.
9. Loose compressor wheel locknut
a) A loose locknut, can lead to premature failure of the turbo.
b) This can be caused by various reasons – worn out bearings caused by oil contamination will result in the rubbing of the compressor wheel against the housing.
c) Under normal conditions, the lock nut will tighten during rotation. However, should the rotor become unbalanced due to worn bearings or foreign objects, the compressor wheel will come in contact with the housing.
d) Under such circumstances, a serious wheel to housing contact may lead to vibration.
e) Thus allowing the lock nut to come loose.

It’s highly recommended to check or replace your turbocharger by an experienced technician or garage. www.refoneturbo.com can supply you all kinds of turbocharger replacement or turbo parts and don’t hesitate to contact us at any time!
 Online Service
Online Service +86 551 65617152
+86 551 65617152 info@refoneturbo.com
info@refoneturbo.com +8618133658728
+8618133658728